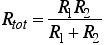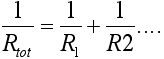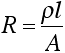- Electrical resistance is the opposition to the flow of electrons in a circuit.
Electrical resistance is present in all parts of an electric circuit
The unit of electrical resistance is the ohm. An ohm is equal to one volt/ampere
Ohm’s law, R = V/I, can be used to solve for resistance (R), voltage difference (V) and current (I) in electrical circuits.
Wire resistance in electrical circuits is similar to fluid resistance in pipes.
The total resistance (Rtot) of two resistors (R1 and R2) connected in series is Rtot = R1 + R2
The total resistance (Rtot) of two resistors (R1 and R2) connected in parallel is 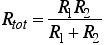 or:
or: 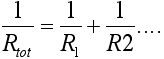 Conductors, semiconductors and insulators are material classifications based on resistivities. Resistivity means the capacity to resist electric current.
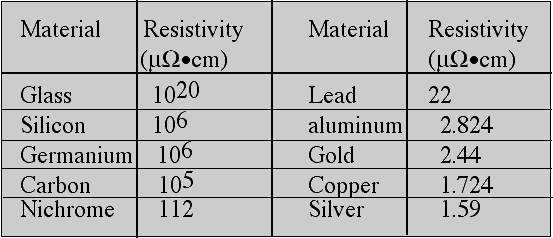
Conductors, semiconductors and insulators are material classifications based on resistivities. Resistivity means the capacity to resist electric current.
Resistivity
- Constant for any material
- Resistance is proportional to the resistivity and length of the material, and inversely proportional to the cross-sectional area of the material.
- Resistance based on resistivity is given by:
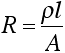
Where:
- R = resistance (W)
- r = resistivity (W·cm)
- l = length (cm)
- A = cross-sectional area (cm2)
|
|